Most people are familiar with the idea of a normal proxy: you send a request to an intermediary server and that server talks to the website on your behalf. This protects your identity, helps bypass restrictions and can cache responses.
A reverse proxy flips this relationship. Instead of hiding clients, it hides and protects your servers. The proxy sits at the edge of your network and receives all incoming web requests, decides which backend server should handle each one and then forwards the response to the client. The origin server never talks directly to the outside world.
Why You Might Need One
Direct Access is Inefficient and Risky
A basic web server sends pages directly to each visitor. This works when traffic is low but quickly becomes a bottleneck or a target.
- Scaling & reliability: Without a reverse proxy, a single server must process every request. Under high load, this machine can become overwhelmed and potentially crash. A reverse proxy can distribute requests across a pool of servers and even send users to geographically closer servers to reduce latency. If one backend fails, the proxy keeps your site alive by routing around it.
- Security & privacy: Exposing your origin server’s IP address makes it easier for attackers to target you directly. A reverse proxy hides the origin address and can block malicious requests as well as minimise DDoS attacks.
- Efficiency: Modern websites often serve large numbers of images, style sheets and scripts. A reverse proxy can cache static content near your users so that subsequent requests do not hit the backend (origin). It can also handle CPU intensive tasks like SSL/TLS encryption, freeing the origin servers to focus on everything else.
Analogy: The Office Receptionist
Think of your server infrastructure like a busy office building. Visitors (web clients) arrive at reception. The receptionist (reverse proxy) greets them, checks if they’re legitimate, and directs them to the right office. They can hand out brochures (cached pages), without having to bother anyone. They also keep the directory private so no one knows exactly where each employee sits. Without a receptionist, every visitor would wander the hallways, interrupting staff, clogging elevators and risking security breaches.
How a reverse proxy works
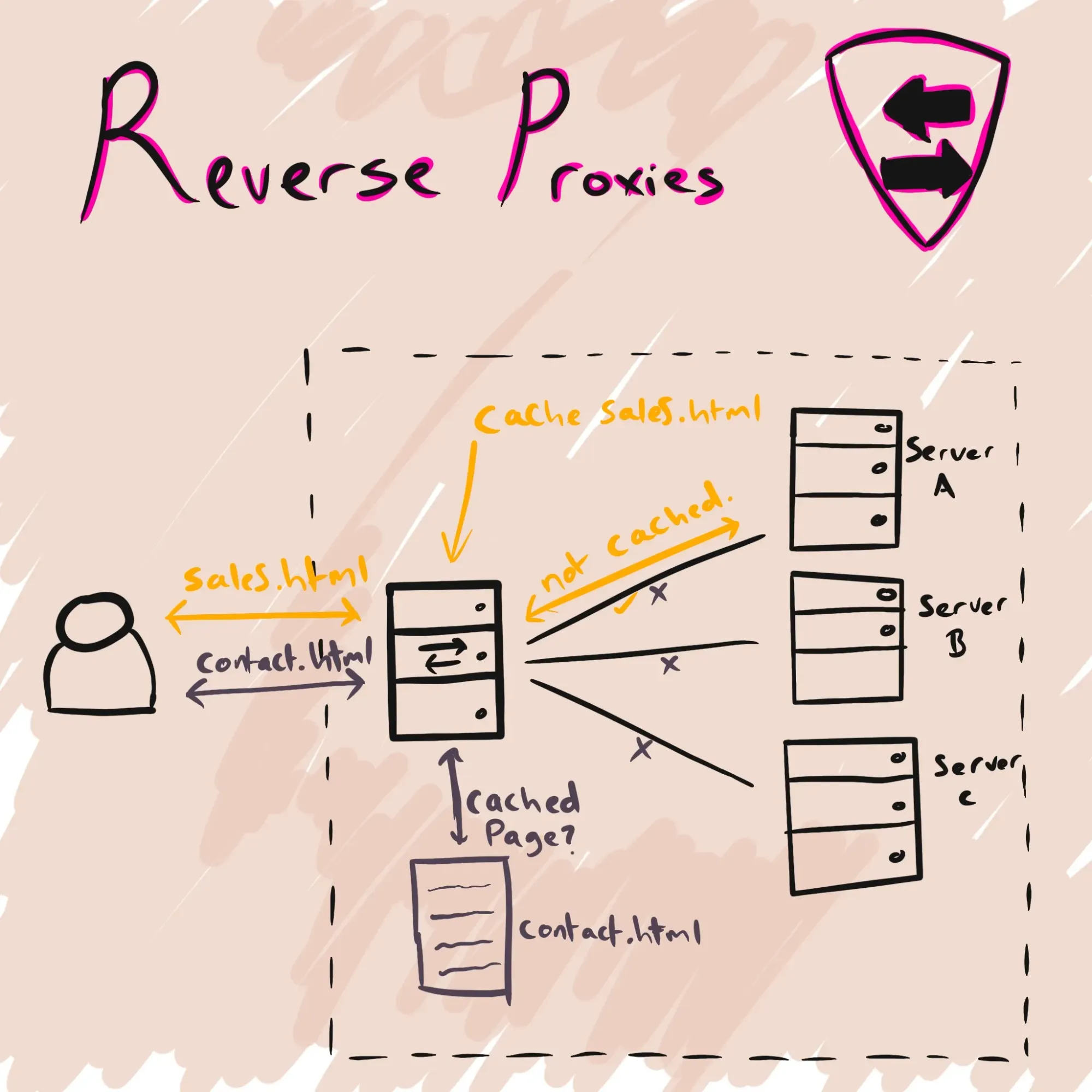
At a high level, a reverse proxy performs the following steps:
- Listen for incoming connections.
- The proxy sits at the network edge and accepts HTTP(S) requests from clients. It may perform a TCP and SSL handshake if the connection is encrypted.
- Inspect and route.
- The proxy examines each request and uses a scheduler to decide which backend server should handle it. Factors include server load, session affinity and geographic proximity. It can also block malicious payloads.
- Optional caching and transformation.
- Before forwarding, the proxy may serve a cached copy of the requested resource or compress the data. It may also terminate SSL, decrypting the request and re‑encrypting the response.
- Forward to the origin server.
- The chosen backend processes the request and generates a response. The proxy receives the response and may cache it for future use.
- Return the response.
- The proxy sends the response back to the client. From the client’s perspective, it’s talking to a single server, even though the content might come from a different machine.
Benefits of Using a Reverse Proxy
- Load balancing & scalability: Reverse proxies can distribute user requests across many servers, preventing any single machine from becoming a bottleneck. Global server‑load balancing sends users to the nearest data centre, further improving performance.
- Caching & compression: Serving cached responses and compressing data reduces latency and saves bandwidth. Cached content is immediately available to users rather than forcing a full round‑trip to the origin server.
- SSL/TLS offloading: Encrypting and decrypting traffic is CPU‑intensive. Offloading SSL to the proxy frees backend servers to focus on application logic.
- Enhanced security: By hiding the origin server’s IP address and filtering traffic, a reverse proxy (such as CloudFlare) reduces the attack surface and can detect malware or DDoS activity. Many organisations layer web application firewalls (WAFs) on top of their proxies for extra protection.
- Central management and monitoring: The proxy provides a single point of control for logging, access control and rate limiting. Admins can analyse request patterns, test new versions and roll out changes centrally.
- Simpler certificate management: The proxy can manage SSL certificates for multiple domains, simplifying renewal and rotation.
- Versatile deployment: Reverse proxies are available as hardware appliances, cloud services (e.g. CDN providers such as AWS, Bunny.net and CloudFlare) or open‑source software like Nginx, Varnish and Traefik.
Trade‑offs and challenges
Reverse proxies bring powerful capabilities but also introduce some drawbacks:
- Single point of failure: If the proxy fails, all services behind it become unavailable. High‑availability configurations and redundant proxies mitigate this risk.
- Risk to stored information: Because the proxy sees all incoming and outgoing traffic, a malicious or compromised provider could log sensitive data like IP addresses and passwords. Choose trusted providers and apply encryption end‑to‑end.
- Configuration complexity: Setting up routing rules, SSL termination, caching and security policies requires careful configuration and maintenance. Misconfiguration can lead to errors or vulnerabilities.
- Susceptible to attacks: Since the proxy is publicly accessible, it can itself become a target for DDoS or HTTP request smuggling. Use DDoS protection and keep your proxy software patched.
- Latency & overhead: The extra hop introduces slight latency. However, caching and compression often offset this.
Where are Reverse Proxies Used?
Reverse proxies are common in many environments:
- Content‑delivery networks (CDNs)
- Providers like Cloudflare place reverse proxies around the world to cache content, offload SSL and absorb DDoS attacks.
- Large web applications and microservices
- Companies deploy proxies in front of clusters of application servers to balance load and provide a single entry point.
- Home labs & self‑hosters
- Enthusiasts use lightweight reverse proxies (e.g. Traefik, HAProxy, Nginx) to expose multiple services under one domain and add automatic Let’s Encrypt certificates. (In fact, this very blog utilises CloudFlare to proxy traffic and protect the origin)
- Security appliances
- Web application firewalls and API gateways often operate as reverse proxies, inspecting requests and enforcing security policies.
FAQ
Does a reverse proxy replace a load balancer?
Not exactly. Load balancing is one of the functions a reverse proxy can perform. Dedicated load balancers focus solely on distributing traffic, whereas reverse proxies also handle caching, security and protocol translation. Even a single server can benefit from the SSL offloading and protection offered by a proxy.
How is it different from a forward proxy?
A forward proxy sits in front of clients, hides their IP addresses and fetches content from the internet on their behalf. Reverse proxies sit in front of servers and ensure that no client communicates directly with the origin.
Do I need a reverse proxy for my personal website?
If you run a small static site with low traffic, a reverse proxy is optional. However, using one (often via a free CDN) can provide TLS termination, caching and basic DDoS protection with minimal effort. For self‑hosted services, tools like Nginx Proxy Manager or Traefik simplify exposing multiple internal services under a single domain.
Can a reverse proxy inspect encrypted traffic?
Yes. When configured for SSL termination, the proxy decrypts incoming traffic, allowing it to inspect content and enforce security policies. The proxy then re‑encrypts the response for the client. If end‑to‑end encryption is required, the proxy can be configured for SSL passthrough, where it simply forwards encrypted traffic to the origin server and does not see the content.







